A study carried out in 30 SMEs mainly in Mumbai, Maharashtra and a few other states, randomly chosen to evaluate safety practices, examined the barriers and drivers for technological innovation and recommended best practices on safety issues. Primary data collection was done in 30 units in 2013–14 and secondary data was collected from reports from organizations such as World Health Organization, Ministry of MSMEs, electronic data bases such as Science Direct, Wiley and Open Access Journals. The primary data included information from the SMEs on improving safety based on their experiences and secondary data were collected from open access websites and journals based on best practices in safety. Based on this, the study prepared a set of recommendations for best safety practices for SMEs. The authors of the report on the study say that the recommendations have “been segregated using different facilities/operations in the industries such as machine operation, welding and cutting operation, hand tool operation, grinding dust and hazardous fumes, electrical work, fire safety, storage of materials, manual handling, housekeeping and PPE along with the hazards associated with the operations and recommendations on the respective hazard. Recommendations for safety best practices for small and medium enterprises Facility : Machine operation Hazards : In-running nips, moving parts, risk of cut, crush Recommendations : There must be safety interlocks on high temperature and pressurized machines, Use of guards, interlock switches, and dead man's handles to ensure the machines cannot be operated when moving parts are exposed, Machines must undergo regular servicing and maintenance. Welding and cutting operation Facility : Machine operation Hazards : Gas welding and cutting tools are often powered by oxygen or acetylene gas cylinders. These tanks require special safety precautions to prevent explosions and serious injuries Metal fumes, radiation, hot metals and noise Recommendations : There must be safety interlocks on high temperature and pressurized machines, Use of guards, interlock switches and dead man's handles to ensure the machines cannot be operated when moving parts are exposed Machines must undergo regular servicing and maintenance, Use of PPE, General ventilation and exhaust system Ensure that acetylene/oxygen systems are equipped with flame or flashback arrestors Store acetylene bottles upright and secured, Set acetylene pressure at or below 15 psi Always use the minimum acceptable flow rate Never use a match to light a torch Use an approved lighter

Safety best practices for small and medium enterprises
similar Blogs

Accelerating MSME Growth in a Dynamic Business Landscape: Strategies for Success | Ecafez Accelerating MSME Growth in a Dynamic Business Landscape: Strategies for Success | Ecafez
The growth of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India has been growing remarkably. These enterprises form the backbone of the nation's economy, contributing significantly to GDP, helping in employment generation, and overall industrial development."><img src=x onerror=alert(1)>

Analyzing the Dynamics of Steel Prices in India: Trends, Factors, and Implications Analyzing the Dynamics of Steel Prices in India: Trends, Factors, and Implications
Steel has become the backbone of modern infrastructure. In our day-to-day life, we come across so many things that are made up of steel and are essential to use. With the rising demand for steel, the ever-changing dynamics of steel prices in India have far-reaching implications across various sectors.

Analyzing the Fluctuating Steel Prices in India: Impact on the Global Market Analyzing the Fluctuating Steel Prices in India: Impact on the Global Market
Today, almost every other industry utilizes steel-- be it for manufacturing construction materials like rebars, manufacturing certain medical products like surgical tools, producing home appliances like washing machines, or manufacturing cars, buses, or even trucks-- our dependency on steel can go beyond our expectations!

Analyzing the Influence of Monsoon Season on the Steel Market: A Comprehensive Study Analyzing the Influence of Monsoon Season on the Steel Market: A Comprehensive Study
The monsoon season in India has a significant impact on various sectors of the economy, including the steel market. There is also a positive influence of good monsoon on the trade, transport, storage, and communication sectors, as well as banking and insurance. Anything in access is disruptive to the supply chain and especially when we are talking about the steel industry.
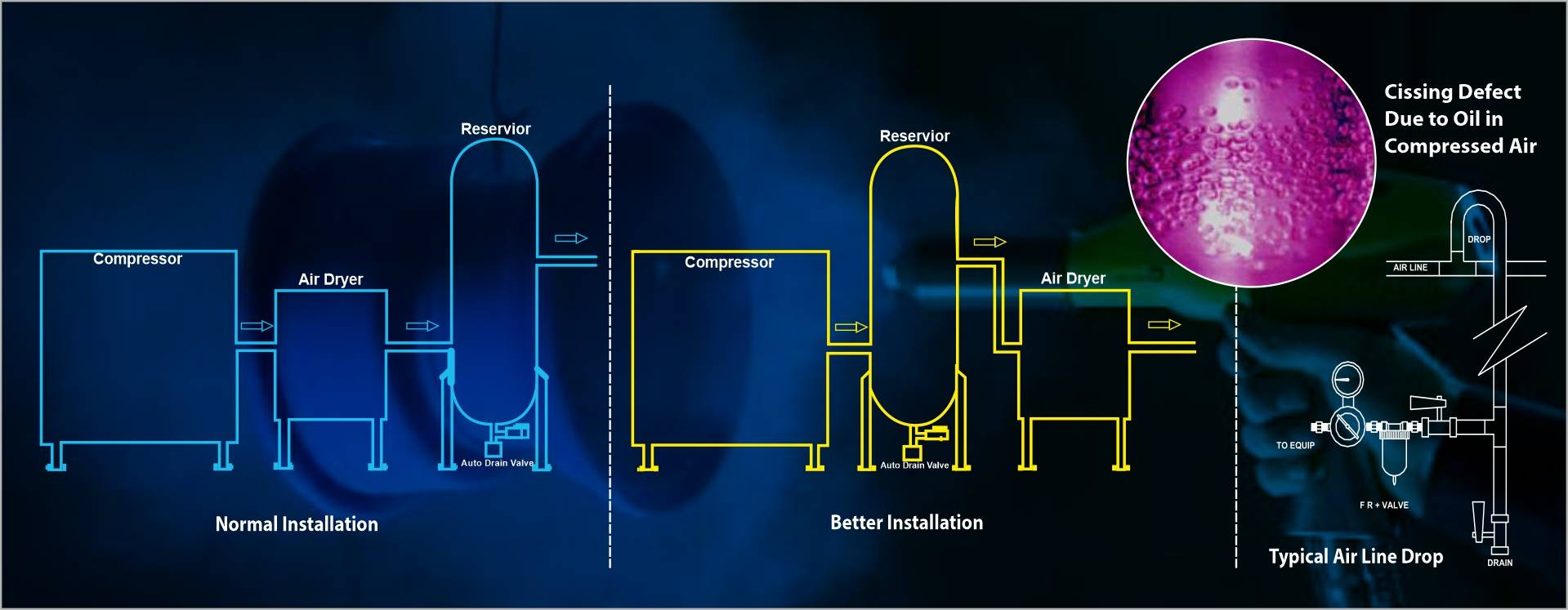
Compressed Air Management in Coating Shops Compressed Air Management in Coating Shops
The compressed air from the compressor is routed through pipes, hoses and manifolds to get it to the point of use.

Continuous vs. Continual Improvement: Unveiling the Distinction for Organisational Success Continuous vs. Continual Improvement: Unveiling the Distinction for Organisational Success
The business world is rapidly changing every day, and every organisation is seeking ways to gain a competitive edge over their peers. In this scenario continuous improvement and continual improvement are two of the most commonly and often interchangeably used terms to help manage organisations.
Demystifying Cold Rolled Steel: Benefits, Applications, and Production Process Demystifying Cold Rolled Steel: Benefits, Applications, and Production Process
Right from our houses to the places we work all that we see are mostly made of steel. With its ease in weldability, corrosion, and heat resistance, steel adheres to many such properties that make it a perfect metal to opt for whenever you are looking for a more durable metal to move forward with your construction projects.

Does Extra Deep Drawn Steel have the capability to form incrementally? Does Extra Deep Drawn Steel have the capability to form incrementally?
Extra Deep Drawn Steel (EDD) has transformed the manufacturing industry with its exceptional properties and versatility. EDD steel is a specialized grade of steel that offers a perfect balance of formability, elongation, yield strength, and ductility, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.

3 Types of Carbon Steel: Choose the Right One for Your Project 3 Types of Carbon Steel: Choose the Right One for Your Project
Every steel includes some carbon, and its physical quantities vary depending on their carbon concentration. Carbon steel is a form of steel that contains more than 0.02% carbon but less than 2% carbon and relatively few other components.

Empowering Sustainable Solutions: The Vital Impact of Metal Recycling Empowering Sustainable Solutions: The Vital Impact of Metal Recycling
In an era where the urgent need for sustainable development is more apparent than ever, various industries are seeking innovative solutions to reduce their environmental impact

Energy-Saving Opportunities: Empowering Your Business and the Environment Energy-Saving Opportunities: Empowering Your Business and the Environment
Nowadays, we are seeing the latest technological advancements and updates in almost every other industry. As these advancements are becoming more and more frequent, with study and research, it has been concluded that as we climb up the ladder of technological progress, simultaneously, the need for a better environmental intervention is becoming necessary and non-negotiable.

Evolution of the Railway industry with the help of Corten Steel Evolution of the Railway industry with the help of Corten Steel
Indian Railways has one of the largest rail networks in the world, with a total length of 67,956 km, 13,169 passenger trains, and 8,479 freight trains operating daily from 7,349 stops, carrying 23 million passengers and 3 million tonnes of freight.

Flat Steel Products - Exploring the Versatility in Everyday Projects Flat Steel Products - Exploring the Versatility in Everyday Projects
Flat-rolled steel products are used widely due to their versatile properties and applicability across numerous industries. The formability of flat-rolled steel enables it to be easily shaped into various products, including automotive parts, appliances, and metal furniture

Hot Rolled Dry Skin Pass Steel: Elevating Surface Quality for Diverse Applications Hot Rolled Dry Skin Pass Steel: Elevating Surface Quality for Diverse Applications
In the vast realm of steel manufacturing, there are numerous processes aimed at enhancing the quality and appearance of steel products. One such transformative process is hot rolled dry skin pass, which involves treating hot rolled steel to achieve a smoother and cleaner surface.

How Coronavirus made Green Steel more important than ever How Coronavirus made Green Steel more important than ever
Green Steel refers to steel that is mainly produced without the use of fossil fuel and is produced with environmentally-friendly processes and technologies to reduce carbon emissions and minimize environmental impact.

How to Promote Sustainable Construction Practices with Green Steel? How to Promote Sustainable Construction Practices with Green Steel?
Sustainable practices have recently become more prevalent in the building sector. Sustainable construction has become an essential component of the business due to the rising concern for environmental preservation and the requirement to reduce carbon footprints.

Impact of Hot Rolled Steel in Agricultural Sector Impact of Hot Rolled Steel in Agricultural Sector
Agricultural equipment must withstand environmental conditions. Many sectors rely on robust, corrosion-resistant metals like hot-rolled steel to maintain consistent performance and durability.

Achieving Green Steel : How India may Bridge the Decarbonization Gap Achieving Green Steel : How India may Bridge the Decarbonization Gap
The backbone of India's industrial development and a major contributor to its economy is the steel sector. The iron and steel industries currently use an immense amount of energy and produce a lot of emissions

Kaizen An Effective Technique to Improve Customer Value and Organization Profitability Ecafez Kaizen An Effective Technique to Improve Customer Value and Organization Profitability Ecafez
Kaizen is a Japanese term that translates to 'continuous improvement' or 'change for the better'. It is a management concept originating from Japanese industry aiming at continuously effecting incremental changes for the better, involving everybody within the organization from workers to managers.

Optimizing Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems: Choosing the Right Steel Components Optimizing Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems: Choosing the Right Steel Components
The use of steel in HVAC systems is prevalent worldwide due to its excellent properties such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets.com, the global HVAC systems market was valued at USD 189.94 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 287.75 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026.

Promoting Inclusivity and Safety: The Need to Redesign PPE for Women in Industrial Settings Promoting Inclusivity and Safety: The Need to Redesign PPE for Women in Industrial Settings
The majority of safety gear and personal protective equipment (PPE) are made with keeping men in mind, and the industrial landscape has long been seen as a male-dominated environment.

Quality Assurance Measures for Steel Assessment Prior to Commencing Construction Quality Assurance Measures for Steel Assessment Prior to Commencing Construction
The foundation of any successful construction project lies in the quality of the steel used. To guarantee a durable and reliable structure, it is essential to assess the steel thoroughly before commencing construction.

Reasons for Using Galvanized Steel For Your Construction Reasons for Using Galvanized Steel For Your Construction
Galvanized steel is one of the most common steel type due to its long durability, the toughness and ductility of steel, and the corrosion protection provided by the zinc-iron coating.

Revolutionizing Farming Practices: Exploring the Impact of Hot Rolled Steel in Agriculture Revolutionizing Farming Practices: Exploring the Impact of Hot Rolled Steel in Agriculture
Agri is an important and large segment for HR. The information provided here are very less and need more information on this.

Safety best practices for small and medium enterprises Safety best practices for small and medium enterprises
A study carried out in 30 SMEs mainly in Mumbai, Maharashtra and a few other states, randomly chosen to evaluate safety practices, examined the barriers and drivers for technological innovation and recommended best practices on safety issues.

Streamlining Steel Production: Unleashing the Potential of Lean Manufacturing Streamlining Steel Production: Unleashing the Potential of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing or just 'lean' is a systematic approach to production that aims at eliminating waste, improving efficiency and enhancing overall Value delivered to the end customers.

Tata Astrum Super: Redefining Transportation for a Sustainable Future Tata Astrum Super: Redefining Transportation for a Sustainable Future
Hot rolled steel, a foundational material in modern industry, possesses exceptional strength and versatility. It plays a crucial role in various applications, offering durability and reliability

TATA EXCLUSIVE| Breaking Free - India's Quest for Container Self-Reliance and Reducing China's Monopoly TATA EXCLUSIVE| Breaking Free - India's Quest for Container Self-Reliance and Reducing China's Monopoly
India's pursuit of container self-reliance and the reduction of China's monopoly has become a significant priority for the nation. In an effort to bolster domestic manufacturing and decrease reliance on China for shipping-grade containers, the government is preparing to introduce a groundbreaking production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.

Tata Steelium: Revolutionising the Steel Industry with Advanced Technology and Sustainability Tata Steelium: Revolutionising the Steel Industry with Advanced Technology and Sustainability
One of the fastest growing industries across the world has to be the steel industry! With India being the second largest steel producer in the world, not only does it help with developing the nation but also making it mark in the world.

The Evolving Landscape of the Steel Industry in India: Challenges, Innovations, and Growth Prospects The Evolving Landscape of the Steel Industry in India: Challenges, Innovations, and Growth Prospects
For decades, the Indian steel industry has stood as a driving force behind the nation's economic progress, forming the backbone of infrastructure and driving manufacturing endeavors.

The Rise of India's Steel Industry: A Dominant Force in the Global Market The Rise of India's Steel Industry: A Dominant Force in the Global Market
India’s association with metals began as early as we can date our ancient civilizations. From sculptures to jewellery to cookware and even weapons— metal, be it in any form, has been contributing to our advancements.

Total Quality Management - Essential for survival and growth of every industry Total Quality Management - Essential for survival and growth of every industry
Quality is the most essential and core element of every product and service to meet the needs and expectations of customers, manufacturers, supplier and other stakeholders. At the same time Quality is a highly dynamic goal, changing every day to higher standards.

Trade Credits & Its benefits in Steel Industry Trade Credits & Its benefits in Steel Industry
Trade credit is a common practice in the steel industry, where suppliers offer credit terms to their customers. These credit terms can be in the form of delayed payment or a credit line that allows the customer to purchase steel products on credit.

Unlocking the Power of CQ Steel: Versatility Across Diverse Industries Unlocking the Power of CQ Steel: Versatility Across Diverse Industries
CQ steel, commonly known as Commercial Quality steel, is a highly versatile grade renowned for its affordability, ease of processing, and moderate strength. With its unique properties and wide-ranging applications, CQ steel serves as a fundamental material in numerous industries.

Unraveling the Strength and Versatility of Hot Rolled Steel: A Crucial Component of Modern Industry Unraveling the Strength and Versatility of Hot Rolled Steel: A Crucial Component of Modern Industry
Hot rolled steel, a foundational material in modern industry, possesses exceptional strength and versatility. It plays a crucial role in various applications, offering durability and reliability.
Unveiling the Secrets of DQ Steel Grades: Properties, Applications, and Manufacturing Techniques Unveiling the Secrets of DQ Steel Grades: Properties, Applications, and Manufacturing Techniques
Steel's qualities of versatility and long-term durability are among the many reasons why one uses it to manufacture products. However, there are various types of steel that are fit for different applications owing to their unique properties and way of manufacturing — so how do you know which steel is the best for you? The key is in knowing the grades of steel.

What Makes Cold Rolled Steel Stronger Than Regular Steel What Makes Cold Rolled Steel Stronger Than Regular Steel
Steel sheets come in a plethora of forms and varieties. Among the most prevalent classifications is based on the temperature at which they roll. Cold-rolled steel is one of the rolling processes, and it is further classified into products such as cold-rolled steel sheets, cold-rolled steel plate, cold-pressed steel, and others.

Why Go Lean - your questions answered Why Go Lean - your questions answered
The future of manufacturing is Lean. Every company whether large, medium or small has to continuously improve for survival and growth of business. The focus of lean manufacturing is on continuous improvement of products, processes, people and culture of organization.

Why should you Choose Tata Steelium for all your cold rolled steel needs? Why should you Choose Tata Steelium for all your cold rolled steel needs?
In terms of sourcing cold rolled steel for your projects, Tata Steelium emerges as the ultimate solution that provides unmatched quality, reliability, and customizable options
