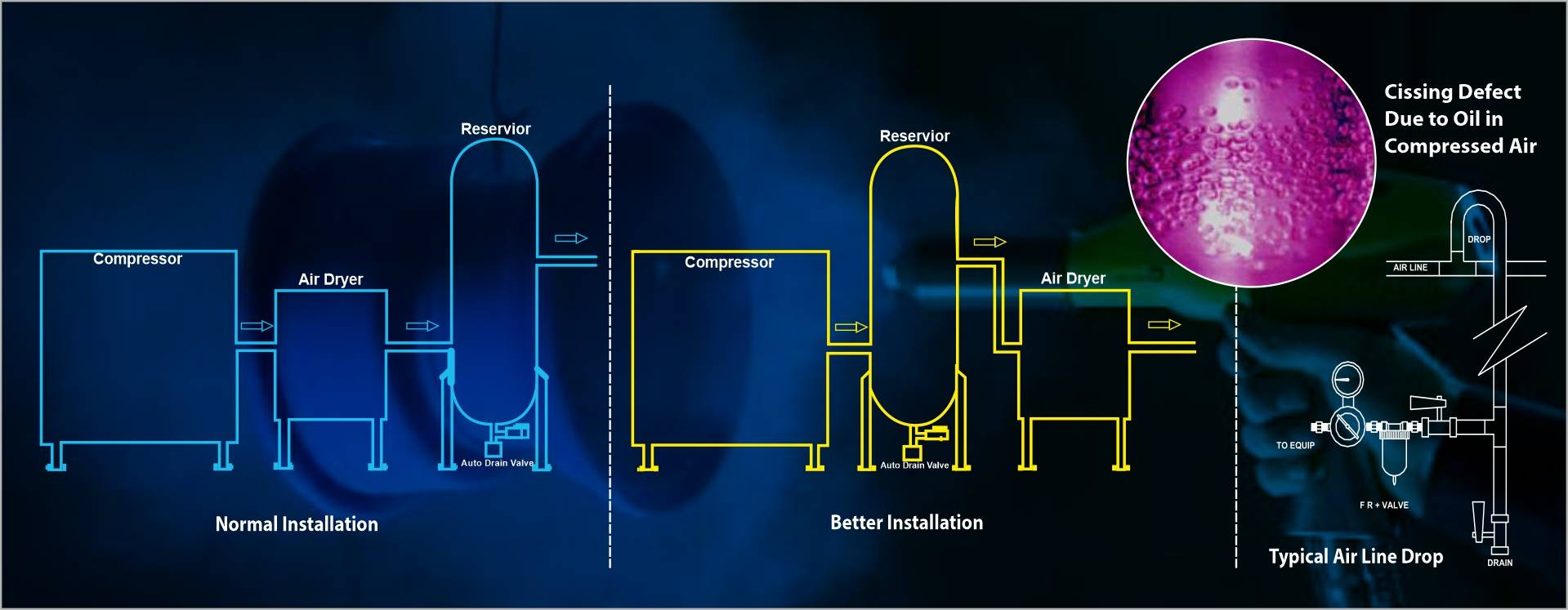
Every steel includes some carbon, and its physical quantities vary depending on their carbon concentration. Carbon steel is a form of steel that contains more than 0.02% carbon but less than 2% carbon and relatively few other components. It is also the most productive metal material. Steel's tensile strength, ductility, and toughness may be modified by adding carbon to it. It is typically used for items that require strength, hardness, and wear resistance, such as cutting tools, steel cables, piano wires, springs, and knives, among other things. The pieces are normally treated and tempered after they have been processed. Steel with a higher carbon content has greater hardness, strength, and wear resistance following heat treatment.
These three kinds of carbon steel are low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel.
Low Carbon steel
Low-carbon steel, often known as "mild steel," is the least expensive choice in terms of value, but it's also simple to bend and shape, making it ideal for a variety of applications such as sheets, screws, and concrete reinforcing bars. It is commonly seen in the kitchen as cookware or dining utensils.
Low carbon steel is easy to weld and form into various shapes, making it ideal for manufacturing processes such as stamping, rolling, and forging. It is also commonly used in applications where strength and hardness are not critical factors, such as in non-structural components of buildings or in household items.
When to Choose Low Carbon Steel
● Steel Frame Building : Low carbon steel, chosen for its particular structural qualities, offers sufficient strength for building frames in construction projects. It satisfies earthquake and wind criteria, is resistant to insects, and is fire and rot resistant.
● Cookware : Carbon Steel is a good choice for a non-toxic, healthy cooking surface. Low-carbon steel, particularly, has the benefit of not rusting and holding an edge, and being sharper for a longer period of time. It also has a greater temperature limit and, once treated, is basically a nonstick substance.
● Pipelines : Low carbon steel is relatively resistant to corrosion, which is important for pipelines that transport liquids and gasses over long distances. This resistance helps prevent the pipeline from corroding and leaking, which can be costly and dangerous.
Medium Carbon
With carbon concentrations ranging from 0.30% to 0.60% of the steel mass, medium carbon steel has a larger carbon-to-iron ratio than low carbon steel. To give high strength, wear resistance, and toughness, medium carbon steels are frequently combined with alloys such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. Most automobile parts are composed of medium carbon steel, which is stronger and more durable than low carbon steel. Medium carbon steel has the following properties: moderate toughness, moderate machinability, medium ductility, medium strength, and medium weldability.
When to Choose Medium Carbon Steel
● Shafts and Gearing : Medium carbon steels have sufficient tensile strength and ductility to allow stock material to be molded into narrow shafts and gears without compromising any of its tensile strength, as well as boilerplates and other tanks with pressured contents.
● Railways : The railway system strongly relies on medium carbon steel for several applications, from manufacturing and engineering, to maintenance, safety, and more. Some common applications include railway wheels, tracks, suspensions, and all other metal-components involved in the railway’ suspension.
● Construction equipment : Medium carbon steel is used in the manufacturing of construction equipment such as bulldozers, excavators, and cranes. Its strength and durability make it ideal for these heavy-duty applications.
High Carbon Steel
As compared to mild and medium carbon steel plates, high carbon steel has the highest strength and hardness. High carbon steel, on the other hand, is less ductile than lower carbon steels, making it considerably more difficult to machine or mold. High carbon steel, like medium carbon steel, can be heat treated to improve hardness and wear resistance for use in applications where steel is subjected to very high levels of stress.
High carbon plate grades have a high carbon content that provides them considerable strength, hardness, and wear resistance, which are essential attributes in applications where steel must consistently withstand intense wear without breaking, such as cutting and chiseling tools.
When to Choose High Carbon Steel
● Automotive: Because of its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high-carbon steel is extensively employed in the fabrication of automobile parts. It has a greater tensile strength than normal steel, thus it can withstand more pressure without shattering or damaging. It's also less prone to fatigue failure, making it an excellent choice for high-stress components including suspension components, engine crankshafts, drive shafts, and differential gears.
● Manufacturing and Construction: Due to its high strength and hardness, high carbon steel makes it ideal for applications where there is high pressure, friction, and wear required. Cutting tools, springs, ball bearings, wire and more and some specified applications.
● Rails: High carbon steel is used to make rails for railroad tracks due to its high strength and durability. It can withstand the weight and pressure of heavy trains passing over it without warping or breaking.
No matter which type of carbon steel you choose, each has their own advantages and disadvantages. It is important to take into consideration the cost, required physical properties and final use when choosing carbon steel.
How Ecafez can help
As a business owner or SME owner, Ecafez contributes to economic progress. Ecafez brands offer a diverse selection of world-class solutions in goods and services adapted to unique needs. Our team is available to users for round-the-clock support to guide and advise them. Our goal is to assist people in getting from where they are to where they wish to go.