Kaizen is a Japanese term that translates to 'continuous improvement' or 'change for the better'. It is a management concept originating from Japanese industry aiming at continuously effecting incremental changes for the better, involving everybody within the organization from workers to managers.
Kaizen is aimed at producing more value with less waste (higher efficiency), creating better working environments, and developing stable processes by standardization.
This never-ending process of achieving continuous improvements within the company every day is in contrast to trying to achieve breakthrough results from a large improvement once in a while. Kaizen as a management technique is therefore more suitable for organizations with a team culture that is trying to achieve long-term gains by incremental contributions from its employees.
Two essential elements of Kaizen:
Improvement or change for the betterContinuity on time scale
Running a business with status quo contains only one element of continuity without any change or improvement. Adapting one time breakthrough technology contains the element of a big or sudden change but without continuity. Kaizen must contain both the elements - improvement and continuity.
Principles of Kaizen:
Human resources are the company's most important assetSuccess cannot be achieved by some occasional radical changes alone, but by incremental yet consistent improvementsImprovements must be based on fact based statistical or quantitative study of the performance of the process.
Thus, under Kaizen, every employee is a valued contributor to the company's success, and must therefore be given the necessary education and training in order to contribute in his or her own way on a continuous basis.
Types of Kaizen
Kaizen can be broadly classified into three categories.
Individual oriented Kaizen:
Employees as individuals have plenty of ideas to make improvements. Individual oriented Kaizen is made in form of suggestions through a suggestion system, which provides a way for the people to suggest new ideas to improve processes and systems.
Group oriented Kaizen:
Quality circle is one of the best examples of group oriented Kaizen wherein a group of people form a voluntary team to make improvements in their work place.
Management oriented Kaizen:
As per the Japanese concept, managers must spend 50 per cent of their time in making improvements through Kaizen activities. It is the management, that has to provide leadership through commitment and involvement for Kaizen, which boosts morale of other employees and presents a real example of the importance of Kaizen.
Kaizen Activities
These provide opportunities to workers to exercise their creative abilities and knowledge while working together to achieve targets and include:
Suggestion System
Frontline workers can put forward suggestions for improvements in products, processes and work. Suggestions that are recognized as effective are put into practice and the person is rewarded.
QC Circle
QC circles are formed by groups of several workers who are engaged in similar tasks, and address problems related to their work and processes. Members meet at defined intervals, discuss problems, develop and implement solutions to make continuous improvements.
Safety Training
Safety training, or KYT (Kiken Yochi Kunren, which means Danger Prediction Training) is conducted mainly for production workers and staff. Before starting an important operation, each worker is fully trained and required to point at the machine he is going to use and say “Yoshi" or OK. In this way, he or she is conscious about professional hazards that may occur during operation, raising safety awareness and preventing accidents.
Total Productive Maintenance
This is conducted to reduce equipment failure rate and shutdowns that affect quality. It contributes to quality assurance and cost reduction by improving equipment availability, productivity and quality performance.
5S Activity
All successful organizations have one common factor; they are neat, clean, organized and uncluttered workplaces or Gemba. Five S improves workers’ efficiency, safety and morale. 5S stands for Seiri (sorting), Seiton (orderliness), Seiso (cleaning), Seiketsu (cleanliness) and Shitsuke (self-discipline). The purpose is to put the workplace in perfect order and maintain discipline for continuous improvement of workplace conditions.
Kaizen Event
A Kaizen event is a concentrated effort, in which a team plans and implements a major process change or changes to quickly achieve a quantum improvement in performance. It is a high-impact, intensely focused, quick-turnaround. In Kaizen events multidisciplinary cross-functional teams work on selected projects to accomplish clearly defined goals in the given timeframe. Duration of Kaizen events generally varies between two to five days.
KAIZEN CASE STUDY
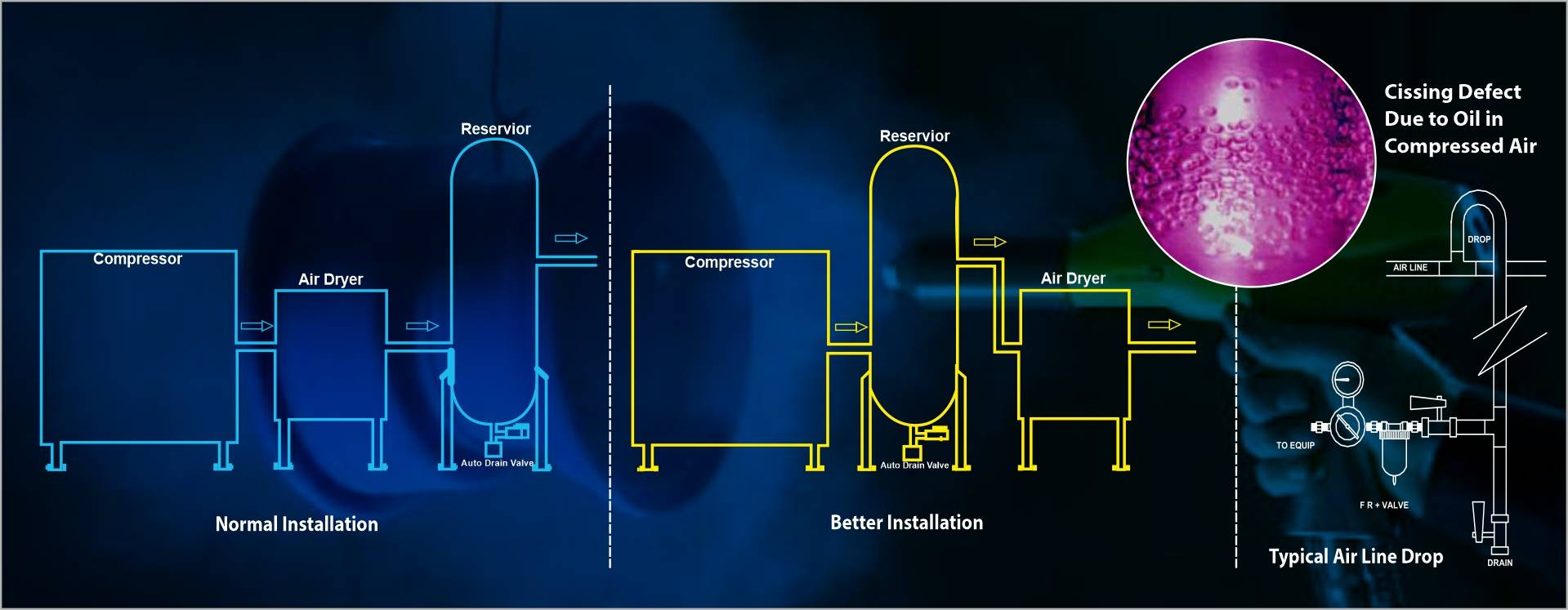
ABC Auto Component Company produces motorcycle battery boxes made of sheet metal and wire components. Its production process includes sheet metal working and welding. During the last few months re-work rate of battery boxes had gone up to 25% due to breakage of weld joints of wire components.
High defect rate and re-working reduced productivity and increased production cost, resulting in failure of on-time delivery.
To solve the re-work problem, Kaizen technique was applied in five phases: Define- Measure- Analyze- Improve -Control, and executed in the following manner:
Define:
Collection of dataProblem defined “Rework rate of battery box increased to 25% during the past month due to breakage of wire clamps welded with battery box body.”Target - bring down rework rate below 5% in 40 days.
Measure:
Process studiedConclusion: Problem related to welding of wire clamp with box bodyCollection of data such as quality of weld wire, quality of welding parameters- electrode quality, current, voltage, operator skill, chemical composition of wire component etc.
Analyze:
Joint analysis of dataCalculation of carbon equivalent of weld joint and study of chemical composition of weld materialsAnalysis revealed that the steel wire used had very high carbon, resulting in formation of brittle weld joint, which was breaking with impact load during handlingTherefore, the root cause of the problem was high carbon content of wire component.
Improve:
Substitute high carbon steel wire with low carbon steel wireThey procured low carbon wires for trial production, closely observing weld quality and breakage rate.Weld joint breakage drastically came down and re-work rate came below 5% in three weeks
Control:
Standardization of steel composition and grade of wire and purchase procedure to ensure prescribed grade material is procured.Developed a standard operating procedure (SOP) for welding, trained all operators and personnel to follow the material and production specification to control quality of weld.