Right from our houses to the places we work all that we see are mostly made of steel. With its ease in weldability, corrosion, and heat resistance, steel adheres to many such properties that make it a perfect metal to opt for whenever you are looking for a more durable metal to move forward with your construction projects.
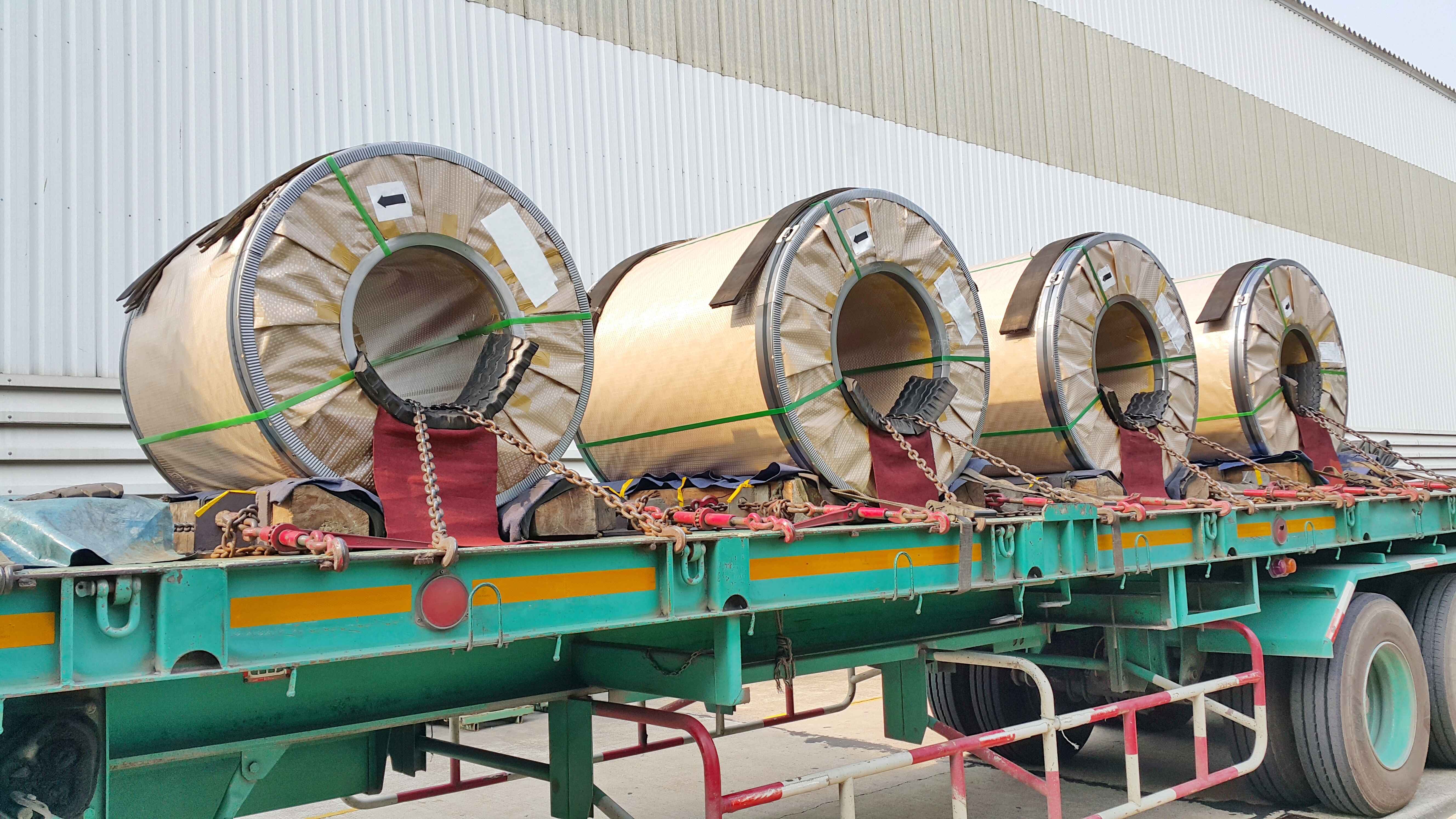
Rolled steel is a method that modifies the shape of the steel, increases its uniformity, and improves the mechanical qualities of materials by using a set of rollers. There are two types of rolled steel: cold-rolled steel and hot-rolled steel. Let us understand what exactly cold-rolled steel is, the difference between cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel, the benefits of cold-rolled steel, and its applications, and briefly understand the process involved that makes this form of steel the most efficient.
What is cold rolled steel?
Cold-rolled steel refers to a variety of steel that goes through a specialized production process under regular temperatures. Unlike hot-rolled steel which gets shaped under higher temperatures, cold-rolled steel uses a method involving rollers that compress it to reduce thickness and enhance its surface texture. This procedure boosts the steel's strength, lifespan, and precision in dimensions, making it fitting for situations where exactness and a refined surface hold utmost importance. Cold-rolled steel sees extensive application in sectors like automotive, construction, electronics, and manufacturing, where its improved qualities assume a pivotal role in yielding a diverse range of commodities.
What’s the difference between Cold-rolled steel and Hot-rolled steel?
To understand both cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel better, let's look into its differentiation based on different categories:
Benefits of cold-rolled steel
Increased Strength: The specialized treatment process that cold-rolled steel undergoes augments its structural robustness, surpassing that of other steel variants. This heightened strength renders it ideal for scenarios demanding resilience and the ability to withstand external pressures.
Exceptional Durability: The refinement in composition during the production of cold-rolled steel translates to elevated durability and a prolonged life cycle. This endurance proves particularly valuable in environments where wear and tear are commonplace, ensuring sustained performance without compromising structural integrity.
Improved Surface Finish: A hallmark feature of cold-rolled steel is its uniform, sleek surface finish. This polished texture elevates its visual allure and qualifies it for applications that prioritize aesthetics. Moreover, the smoother surface contributes to reduced friction and an improved ability to resist corrosion.
Heightened Precision: Cold rolling imparts meticulous dimensional precision to the steel, resulting in uniformity and compatibility within intricate designs or systems. This heightened accuracy holds particular significance in industries where precise measurements are a prerequisite.
Ease of Application: Cold-rolled steel's refined grain structure translates to enhanced formability and workability. This quality streamlines the shaping and manipulation of the material into desired configurations without compromising its inherent strength. As a result, manufacturers can seamlessly fashion intricate designs and structures.
Applications of cold-rolled steel
Automotive Domain: Cold rolled steel finds purpose in crafting vehicle essentials like body panels, frames, and structural components. Its blend of strength, malleability, and precision elevates vehicular safety and integrity.
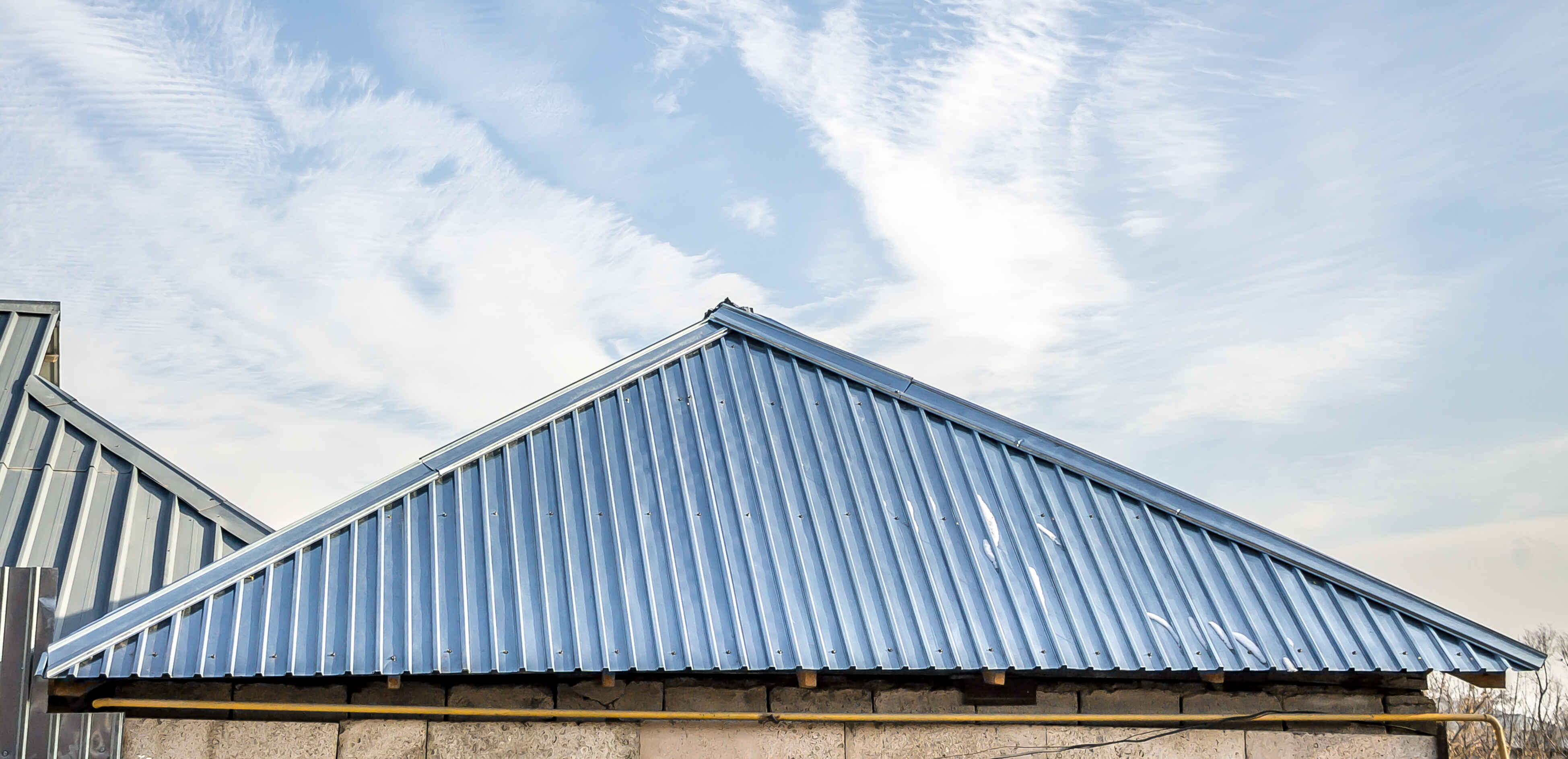
Construction and Architectural Endeavors: Within construction, cold rolled steel takes on roles in roofing, cladding, and structural support due to its resilient nature, visual allure, and resistance to corrosive forces. Architectural accents also benefit from its smooth facade.
Electronics for Consumers: Cold rolled steel's polished exterior makes it a preferred choice for encasing electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and household appliances. Its seamless blend of aesthetics and safeguarding capabilities enhance product design.
Manufacturing and Machinery Sectors: The manufacturing realm employs cold-rolled steel for crafting robust industrial equipment, machine parts, and precision tools. Components such as gears, bearings, and shafts harness its durability and precise dimensions.
Furniture Creation: Modern furniture designs benefit from cold rolled steel's sleek appearance, strength, and flexibility to adopt various shapes. Tables, chairs, and shelving units exemplify the fusion of form and function.
Processes involved in Cold-rolled Steel Production
Initial Rolling and Cleansing: Steel is molded into coils under high temperatures.
Impurities and scales are removed through a cleansing process.
Subsequent Cold Rolling: The pickled coils undergo mechanical compression via rollers. This reduces steel thickness and augments its mechanical attributes.
Enhancing through Annealing: Steel is subjected to controlled heating followed by gradual cooling. This procedure refines the grain structure, elevating the steel's malleability.
Final Touches and Coating: The surface is meticulously cleaned to eliminate residual elements. Additional coatings can be applied to tailor specific properties.
Quality Control: Stringent assessments are implemented to ascertain adherence to predefined standards.
Packaging and Distribution Preparations: Finished steel is precisely cut and packaged, primed for distribution to various destinations.
Let DigEca help you select the best-suited steel for all your projects
DigEca offers a structured method of managing and conducting business that allows tracking buy orders, inquiries, and reports. DigECA will make sure you have all the help you need, not just answers to your questions. Contact an executive through the portal.